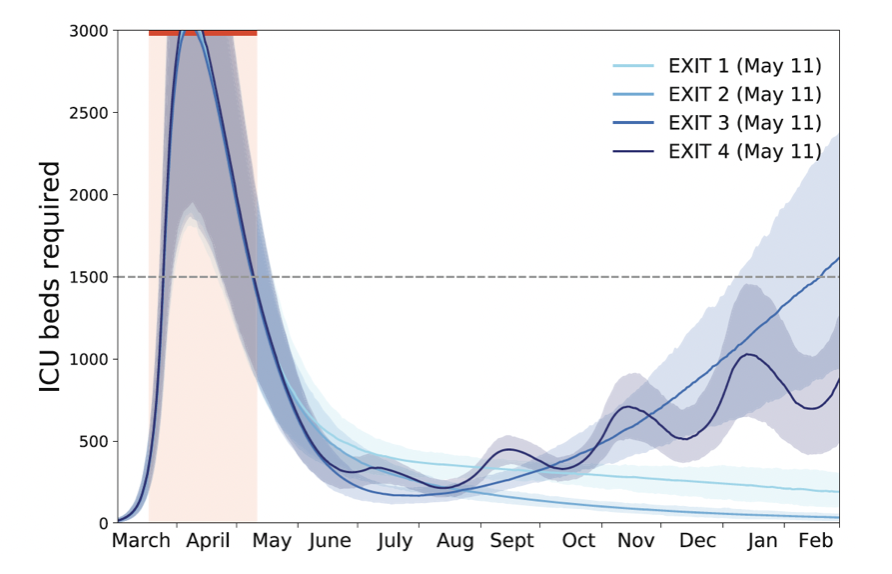
OUTBREAK preparedness AND responseInfectious disease modeling is a powerful tool for epidemic and pandemic assessment and control. We develop advanced data-driven transmission models to anticipate epidemic trajectories and to quantify the effectiveness of interventions. We provide actionable outputs to inform public health policies and improve outbreak response and planning for current and future health crises.
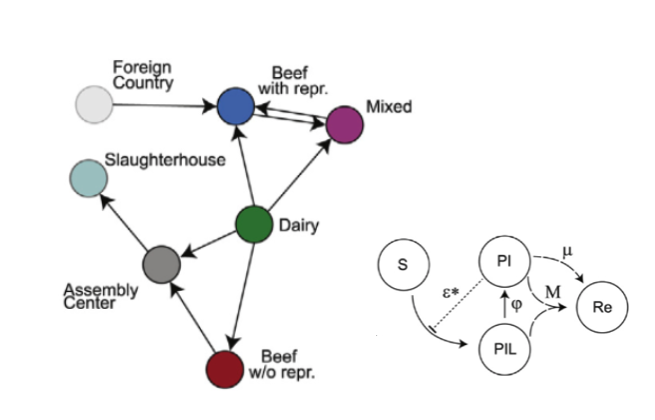
COVID-19 pandemic response. ANIMAL INFECTIONSAnimal diseases represent an important threat for human health due to risk of zoonosis. Focusing on infections in livestock and wild animals, we characterize epidemic risk and disease persistence using large datasets on livestock movements and network-based modeling approaches.
|
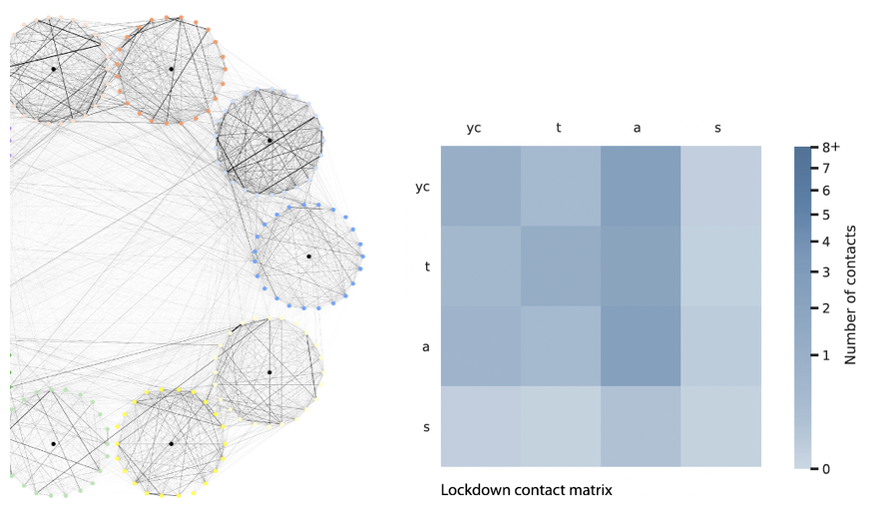
CONTACTS AND BEHAVIORSModeling social contacts and adaptive human behavior during an epidemic is a key challenge. We leverage data on contacts collected through sensors and surveys in the form of contact networks and matrices, to inform agent-based and age-structured models and assess the efficacy of control measures in specific settings or in the community. We aim at characterizing behavioral changes, e.g. in adherence to public health interventions, and study their impact on the epidemic.
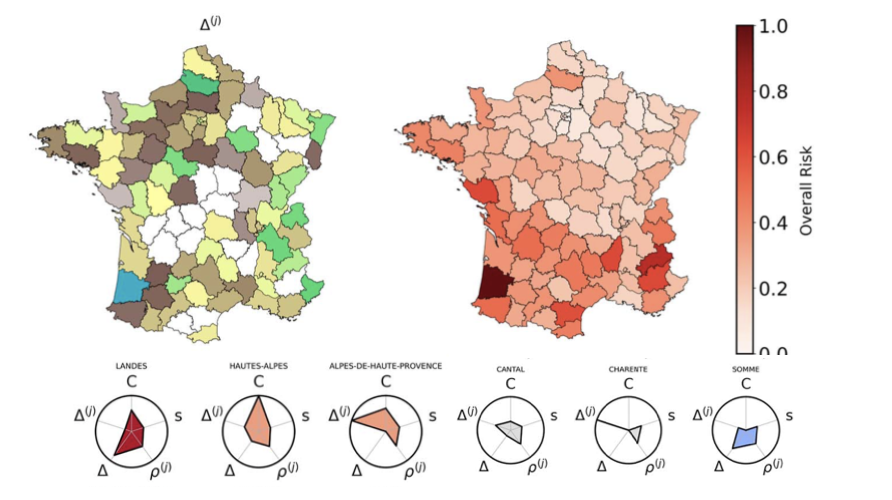
MOBILITYMobility is a key driver in epidemic diffusion. Assessing the spatial invasion and risk associated with geographical areas is critical to design effective public health responses. We integrate mobility data (e.g. from mobile phones) into mathematical models to simulate population's movements and trajectories across space, down to the scale of individuals.
|
DIGITAL SURVEILLANCEDisease surveillance is fundamental to monitor epidemic activity and inform control. Next to traditional systems, novel platforms for digital surveillance in France and across Europe allow to monitor in real time seasonal influenza and COVID-19, providing incidence estimates and valuable insights on e.g. health-seeking behaviors.
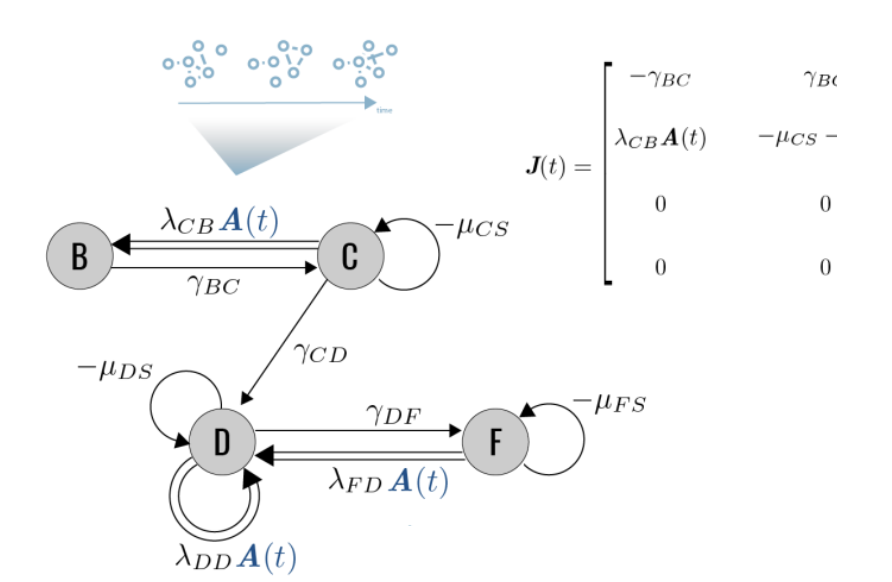
Theory of epidemics on temporal networksThe interplay between time-evolving contact networks and disease time scale influences conditions, speed and routes of epidemic spread. We develop theoretical frameworks to analytically compute the epidemic threshold on temporal networks from arbitrarily complex data on contacts, disease and control efforts.
|
EPIcx lab, 27 rue Chaligny, 75012, Paris, France
INSERM - Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale
Sorbonne Université, Faculté de Médecine
IPLESP UMR-S 1136, site Hôpital St Antoine
INSERM - Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale
Sorbonne Université, Faculté de Médecine
IPLESP UMR-S 1136, site Hôpital St Antoine